Main Concept
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science dedicated to solving cognitive problems that would normally require human intelligence, such as understanding and generating human language, recognizing images and video content, making predictions based on data, identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and providing recommendations.
Key Aspects
Artificial Intelligence involves the following elements and processes:
- A Training Dataset: The data used to train a model. It can vary significantly in size (sometimes huge amounts, but not necessarily), and can be labeled (supervised learning) or unlabeled (unsupervised/self-supervised learning), depending on the training approach and model type.
- The process of Training a Model: with a variety of AI Algorithms and Methods
- A Data Scientist: The person who trains the model with the training dataset.
- The User who uses the Trained Model to obtain some response from it, this is known as inferencing.
Examples
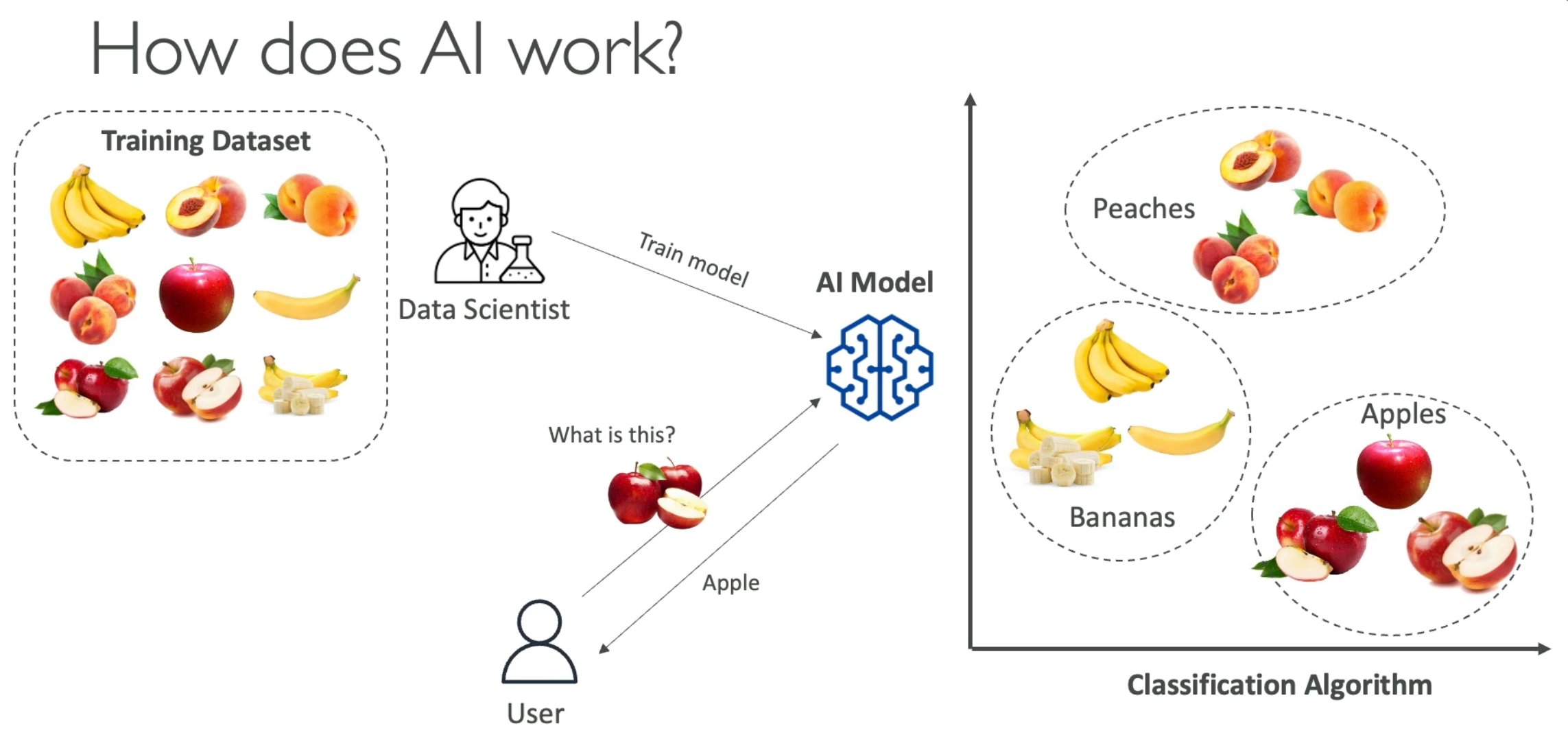
Basic Example
A basic example of an AI model could be a fruit classification algorithm trained on a large dataset of labeled fruit images. A user can then input a new image, and the model would classify what type of fruit it is, even without having seen that exact image before.
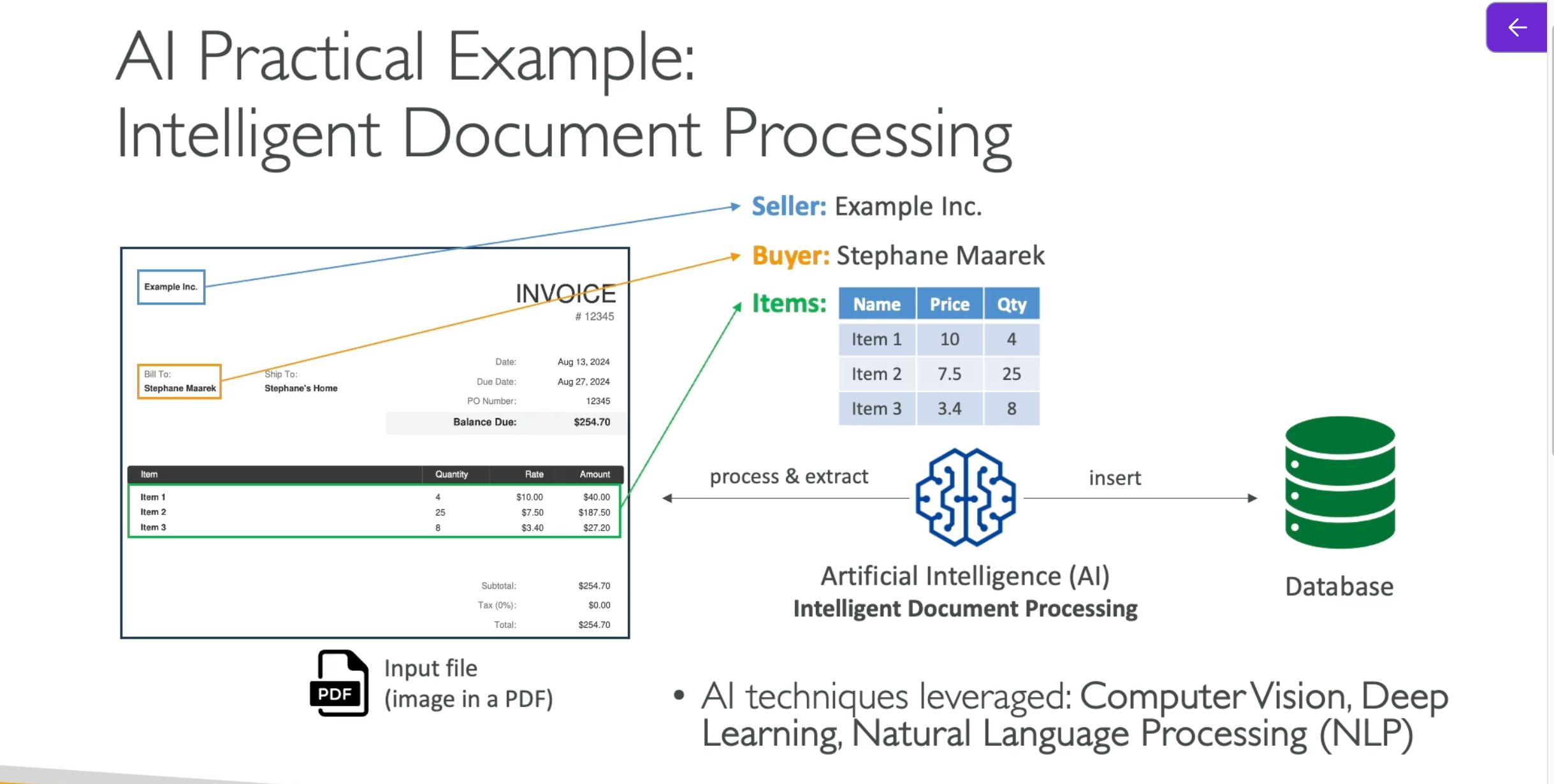
AI Practical Example
Another practical example: An Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) system. When you have invoice images stored in PDF files, AI can extract data from these invoices for further processing. You could use different AI subdisciplines such as Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, and Deep Learning to understand image features. This is already possible with current services and technologies.
AI Subdisciplines
Reflection Questions
- Q: What is human intelligence?
- Q: What are cognitive problems?
- Any tasks that requires thinking, memorizing, analyzing, reasoning, etc..
- Q: So, what is a Model?